4. Creating Distribution Groups
In
Exchange Server 2007, distribution groups serve two primary purposes.
They can be used as email distribution lists that allow messages to be
sent to multiple users with a single address entry, or as security
groups to assign permissions for a shared resource.
To
manage distribution groups on a computer that has the Mailbox server
role installed, you must be logged on as a member of the Exchange
Recipient Administrators group. You must also be a member of the local
Administrators group on that computer.
When a new distribution group is created, a new mail-enabled group object is created within Active Directory.
Note
Whether
you are creating a distribution group solely for the purpose of email
distribution or a security group that is capable of being used both for
email distribution and for assigning permissions, the creation process
is the same and both types are created
as mail-enabled objects. When possible, create a single, mail-enabled
security group to provide both security and distribution group
functionality, rather than two separate groups for the same list of
users.
When creating a
distribution group, the naming convention can be somewhat confusing; it
doesn’t matter if you are creating a Universal Distribution group or a
Universal Security group—you still click the New Distribution Group
button. To create a new distribution group:
1. | Start the Exchange Management Console.
|
2. | In the console tree, select Recipient Configuration.
|
3. | In the action pane, click New Distribution Group. The New Distribution Group Wizard appears.
|
4. | On the Introduction page, click New Group, and then click Next.
|
5. | On the Group Information page, complete the following fields:
- Group Type—
To create a distribution group, select Distribution. To create a
security group, click Security. The remaining steps are identical,
regardless of which type of group you create.
- Organizational Unit—
By default, the New Distribution Group Wizard displays the Users
container in the Active Directory service. To change the default
organizational unit (OU), click Browse, and then select the OU you want.
- Group Name— Type the group name you want.
- Group Name (pre-Windows 2000)—
By default, the group name for pre-Windows 2000 operating systems is
automatically generated to be the same as the group name. You can
modify the name in this field.
- Display Name— By default, the display name is the same as the group name. You can modify the name in this field.
- Alias— By default, the alias is the same as the group name. You can modify the name in this field.
|
6. | Click Next.
|
7. | On
the New Distribution Group page, review the Configuration Summary. To
make any configuration changes, click Back. To create the new
distribution group, click New.
|
8. | On
the Completion page, the summary states whether the distribution group
was successfully created. The summary also displays the Exchange
Management Shell command that was used to create the distribution group.
|
9. | Click Finish.
|
Note
On
the Completion page, although it is not possible to highlight and copy
the Exchange Management Shell command that was utilized to create the
object, you CAN click Ctrl+C to copy the contents of the page. These
contents can then be pasted into a text file, allowing you to save the
EMS command for future use without the GUI interface. This can be
extremely helpful when you need to perform repetitive tasks because you
can perform the task once in the GUI interface, and then copy and
modify the shell command to perform the task repeatedly for your other
items.
Dynamic Distribution Groups
Distribution
groups can also be dynamic in nature. These groups provide the same
functionality as a standard distribution group, but the membership of
the group is built based on a Lightweight Directory Access Protocol
(LDAP) query that you have defined. For example, you could build a
dynamic distribution group that is intended to include all recipients
in a particular state. Each time the list is accessed, the membership
would be built based on information gathered from the Active Directory.
Dynamic
distribution groups require less maintenance than standard groups, as
the query is defined once, and the membership is built automatically
every time the group is called. However, there is a performance cost
associated with their use, especially if the query produces a large
number of results. Every time an email is sent to a query-based
distribution group, server and domain resources are utilized to
determine its membership. Dynamic distribution groups are an extremely
functional tool, but should be used with discretion. To create a new
dynamic distribution group:
1. | Start the Exchange Management Console.
|
2. | In the console tree, select Recipient Configuration.
|
3. | In the action pane, click New Dynamic Distribution Group. The New Dynamic Distribution Group Wizard appears.
|
4. | On the Introduction page, click Next to continue.
|
5. | On the Group Information page, complete the following fields:
- Organizational Unit—
By default, the New Distribution Group Wizard displays the Users
container in the Active Directory service. To change the default
organizational unit (OU), click Browse, and then select the OU you want.
- Group Name— Type the group name you want.
- Display Name— By default, the display name is the same as the group name. You can modify the name in this field.
- Alias— By default, the alias is the same as the group name. You can modify the name in this field.
|
6. | Click Next.
|
7. | On
the Filter Settings page, you will configure the filter that is used to
select the recipients for the dynamic group. If you want to limit the
membership to only users, resources, mail-enabled groups, or contacts,
you can select any combination of them on this screen. When you are
ready, click Next to continue.
|
8. | On
the Conditions page, you can select the conditions that will build the
LDAP query that will identify the recipients to be included in the
list. When you are ready, click Next to continue.
|
9. | On
the New Dynamic Distribution Group page, review the Configuration
Summary. To make any configuration changes, click Back. To create the
new dynamic distribution group, click New.
|
10. | On
the Completion page, the summary states whether the distribution group
was successfully created. The summary also displays the Exchange
Management Shell command that was used to create the distribution group.
|
11. | Click Finish.
|
5. Managing Distribution Groups
As
organizations grow, they might find that the number of distribution
groups that are maintained can get extremely large. As the membership
of these groups can change often, the maintenance of them can take a
significant amount of administrative resources. Because of this,
Exchange allows administrators to delegate the management of
distribution groups to users who they designate.
Delegating Management of Distribution Groups
Often,
after a distribution group has been created, an administrator can
delegate the maintenance of the group membership to another user. For
example, if the manager of a project team has constantly shifting
resources reporting to her, the management of the distribution group
might be relinquished so that she can update it as necessary. To
delegate the management of a distribution group:
1. | Start the Exchange Management Console.
|
2. | In the console tree, click the Recipient Configuration node, and then select Distribution Group.
|
3. | From the results pane, select the distribution group you want to manage.
|
4. | In the action pane, click Properties.
|
5. | Select the Group Information tab, and place a check mark in the Managed By check box.
|
6. | Click Browse, and select the appropriate recipient to manage the distribution list.
|
7. | Click OK to save the changes and exit.
|
Distribution List Mail Flow Settings
Often,
distribution lists are created with a specific user base in mind. For
example, although you might want any employee in the company to be able
to send to your “Employee Suggestions” mailbox, you probably would want
to restrict who can send to “All Employees,” or “All District Managers.”
To restrict who can send to a particular distribution group, perform the following actions:
1. | Start the Exchange Management Console.
|
2. | In the console tree, click the Recipient Configuration node, and then select Distribution Group.
|
3. | From the results pane, select the distribution group you want to manage.
|
4. | In the action pane, click Properties.
|
5. | Select the Mail Flow Settings tab, and then double-click the Message Delivery Restrictions option.
|
6. | Click the Browse button, and select the appropriate recipient to manage the distribution list.
|
7. | Click OK to save the changes and exit.
|
When
an unauthorized sender creates and sends an email to a restricted
distribution group, a message similar to the one shown in Figure 6 will be seen by the sender.
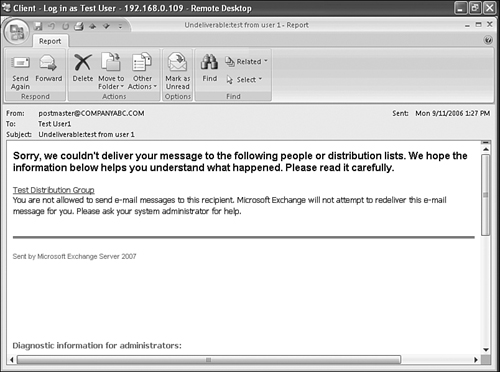
As
you can see, the message generated by Exchange Server 2007 is much more
friendly and informative than the nondelivery reports (NDRs) sent by
previous versions of Exchange.
Other
delivery restriction options include Require That All Senders Are
Authenticated, which prevents anonymous users from sending messages to
the distribution group, and Reject Messages From, which allows you to
configure specific users or groups that are restricted from sending
messages to the group. In addition, message size restrictions can be
placed on the distribution group, only allowing messages smaller than
the mandated size to be delivered.