1. Compression: How It Works, How to Use It
Windows 7 ships with built-in provisions
for file compression that is implemented via NTFS. File compression
works by encoding data to take up less storage space. Digital data is
compressed by finding repeatable patterns of binary 0s and 1s. The more
patterns found, the more the data can be compressed. Text can generally
be compressed to approximately 40% of its original size and graphics
files from 20% to 90%. Some files (namely EXE files) compress very
little because of the lack of repeating data patterns within the
program. The amount of compression depends entirely on the type of file
and compression algorithm used.
Compressing a file or folder in Windows is a simple process:
1. | Open Windows Explorer and select the file or folder you want to compress.
|
2. | Right-click and select Properties from the context menu.
|
3. | Click the Advanced button at the bottom of the Properties dialog box.
|
4. | In the Advanced Attributes dialog box that appears, check the Compress Contents to Save Disk Space box (refer to Figure 1).
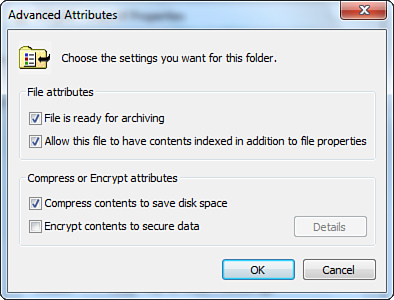
|
5. | Click
OK, and you are prompted to choose whether you want to compress files
and folders (if you’re compressing a folder) recursively. Doing so is
generally desirable and a safe bet.
|
Two caveats are in order with compression:
A file or folder can be compressed or encrypted, but not both. These options are mutually exclusive.
Caution
When
using compression, keep in mind some disk space requirements. If you
try to compress a volume that’s running extremely low on free space,
you might see this error message: Compression Error
File Manager/Explorer cannot change compress attributes for:
"path\filename" This
error message indicates that the system needs additional free space to
perform compression. The system is not designed to manipulate the data
in place on the disk. Additional space is needed to buffer the user
data and to possibly hold additional file system metadata. The amount
of additional free space required depends on the cluster size, file
size, and available space. |
By
default, compressed files are shown in blue and encrypted files are
shown in green. If you choose Control Panel, Folder Options and select
the View tab, you can find an option to display compressed and
encrypted files or folders in an alternate color.
Use
compression only when expressly needed. Compression causes significant
performance reduction if a sizeable number of commonly accessed files
are compressed, due to the CPU processing required to decompress them
for use.2. Third-Party Management Tools
Table 1
provides a list of tools that you should not be without if you are
serious about hard disk tweaking, backup, and recovery. By searching on
the Web, you can easily find any of these popular programs. To
determine which versions of a particular tool are compatible with
Windows 7, contact the software vendor.
Table 1. Third-Party Disk Management Tools
| Type of Program | Vendor | Product Name |
|---|
| Data Recovery | Ontrack | EasyRecovery DataRecovery |
| | Iolo | Search and Recover |
| | Diskeeper | Undelete |
| Disk Management | Acronis | Acronis Disk Director Suite 10 |
| | Symantec | PartitionMagic |
| | Avanquest Software | Partition Commander |
| Professional Compression (Zip file) | ConeXware | PowerArchiver |
| | WinZip International LLC | WinZip |
| | PKWare | PKZip for Windows |
| | FileStream, Inc. | TurboZIP |
| | Info-Zip | Info-Zip |
| | Win.rar GmbH | WinRAR |