1. Applying Fills and Outlines
Text boxes are just like any other object in their
fill and outline formatting.
The fill is the center of the text box, and the outline
is the border. Each can have separate formatting. For example, you can
have a transparent fill with a solid border or vice versa. You can apply
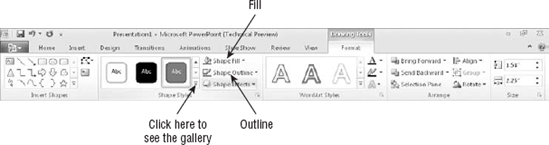
one of the Shape Styles presets from the Format tab to apply both at
once, or you can adjust them separately with their respective menus on
the Format tab. See Figure 1.
To apply one of the presets, click it, or open the
gallery if the one you want doesn't appear. At the bottom of the gallery
is Other Theme Fills, as shown in Figure 1. The fills on this submenu are the same as the background fills available from the Design tab.
If you switch themes such that the background fill presets change, the
background of the text box changes, too, if it is formatted with one of
these.

For the fill,
you can choose a solid color, a gradient, a picture, or a texture. For
the outline, you can select a color, thickness, and dash style.
Selecting one of the background fills in Figure 7-15 fills the text box separately with one of the background presets. It does not necessarily pick the same
background preset as is applied to the slide master. If you want the
text box to always have the same fill as the current background, you can
either leave it set to No Fill (the default fill), or you can set its
fill to match the background:
Right-click the text box and choose Format Shape.
Click Fill if it is not already selected.
Click Slide Background Fill.
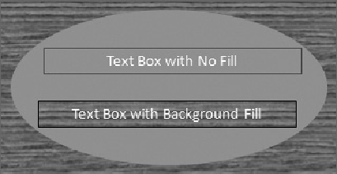
There is only one minor difference between No Fill
and a Slide Background Fill. If there are any objects stacked behind the
text box, the text box obscures them when set to Background, but shows
them when set to No Fill. Figure 3 shows the difference for two text boxes placed on a wood grain background with a filled oval overlaid.
NOTE
After you've set the text box's fill to
Background, the Shape Styles presets no longer work on it until you go
back into the Format Shape dialog box and set the fill to Solid Fill or
one of the other fills.
2. Setting Fill Transparency
Fill transparency
determines how much of the background (or whatever is layered behind the
text box) shows through it. By default, it is set to 0, which means the
text box is not transparent at all when it has a fill assigned to it.
To set the fill transparency, follow these steps:
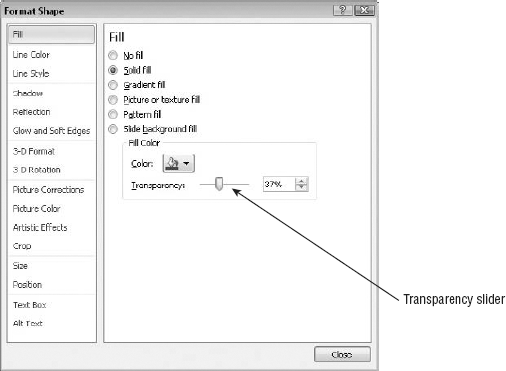
Right-click the text box and choose Format Shape. The Format Shape dialog box opens.
Click Fill if the fill controls are not already displayed. See Figure 4.
Drag the Transparency slider or enter a percentage in its text box.
|
If the fill is a gradient, you must set the transparency separately for each of the gradient stops. (A stop
is a color in the gradient.) Set the Gradient Stops drop-down list to
Stop 1, adjust the transparency, set it to Stop 2, adjust the
transparency, and so on.
|
|
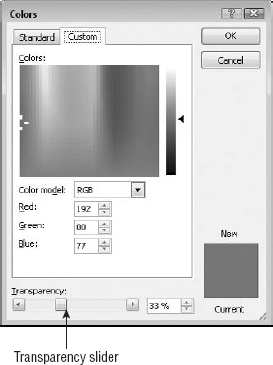
There is another way to set transparency, but it only works when you are applying solid fixed colors as follows:
On the Drawing Tools Format tab, click Shape Fill and choose More Fill Colors.
Select the desired color.
Drag the Transparency slider at the bottom of the dialog box to a new value, as shown in Figure 5.